
When the body's immune tolerance mechanism is broken, the immune system regards its own tissues and organs as foreign bodies, and produces abnormal immune responses against the tissues and organs, resulting in body damage. Such diseases are called autoimmune diseases. After the human body produces abnormal immune responses, B cells will secrete immunoglobulins against their own tissues and organs, also known as autoantibodies. The reasons for the production of autoantibodies are complicated, and there are three commonly accepted production mechanisms, namely, the release of antigen/cryptic antigen, the change of epitope, and molecular simulation. Since most autoimmune diseases have complex clinical symptoms, the detection of autoantibodies undoubtedly provides clinicians with more evidence for the diagnosis of the disease.
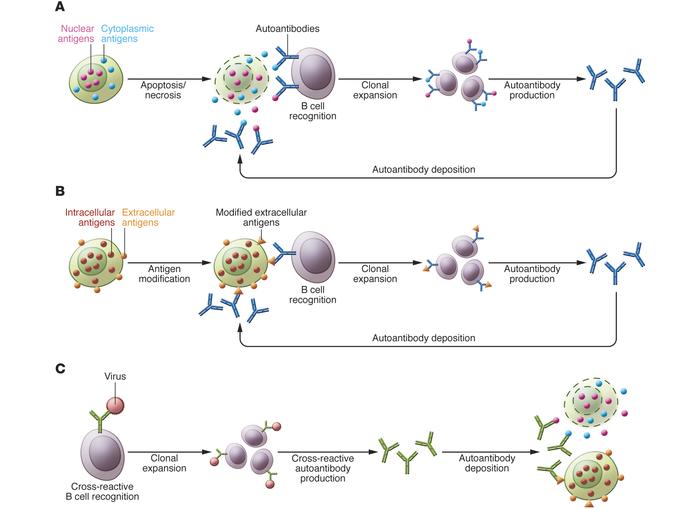 Fig.1 Three models can explain the recognition of intracellular antigens by autoantibodies. (Suurmond J, and Betty D. 2015)
Fig.1 Three models can explain the recognition of intracellular antigens by autoantibodies. (Suurmond J, and Betty D. 2015)
Diagnosis Method
Detection methods for autoimmune diseases:
- Autoantibody test. Including anti-nuclear antibody spectrum, rheumatoid arthritis-related autoantibody spectrum, anti-phospholipid antibody spectrum, anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibody spectrum, autoimmune liver disease-related antibody spectrum, etc. There are many methods for autoantibody tests, including indirect immunofluorescence, enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, radioimmunoassay, western blotting, immunoprecipitation, etc. Each antibody test can use one or several methods for detection. Choose the appropriate examination according to the patient's medical history and symptoms. Some healthy people may also be positive for antibodies, so autoantibody examination cannot be used as a basis for diagnosis alone. It needs to be diagnosed in combination with clinical manifestations, medical history and other tests.
- Immune complex and complement test. During active periods, some autoimmune diseases may increase circulating immune complexes and decrease serum complement levels
- Cross antigen test. Certain viral or bacterial infections can cause autoimmune diseases. For example, streptococcal infection can cause rheumatic heart disease. The cause can be determined by testing for cross-antigens.
- Detection of lymphocyte number and ratio. Immune disorders and other immune system dysfunctions can lead to autoimmune system diseases. The immune system can be assessed by lymphocyte count, T cell count, B cell differential count and CD4/CD8 subgroup ratio determination. Flow cytometry is often used for detection.
- Pathological examination. Selective biopsy based on the patient's symptoms and history plays a decisive role in the diagnosis of many autoimmune diseases.
Diagnosis Products of Autoimmune Disease
Creative Biogene has a professional team of experts who developed quality autoimmune disease diagnostic products. Our products are competitive in the market due to their reasonable price and high quality, which can help you solve the diagnosis problem quickly. We look forward to working with you for your cooperation.
Please contact us for more details.
References
- Suurmond J, and Betty D. (2015). "Autoantibodies in systemic autoimmune diseases: specificity and pathogenicity." The Journal of clinical investigation. 125.6: 2194-2202.
For research use only. Not for any other purpose.

 Fig.1 Three models can explain the recognition of intracellular antigens by autoantibodies. (Suurmond J, and Betty D. 2015)
Fig.1 Three models can explain the recognition of intracellular antigens by autoantibodies. (Suurmond J, and Betty D. 2015)